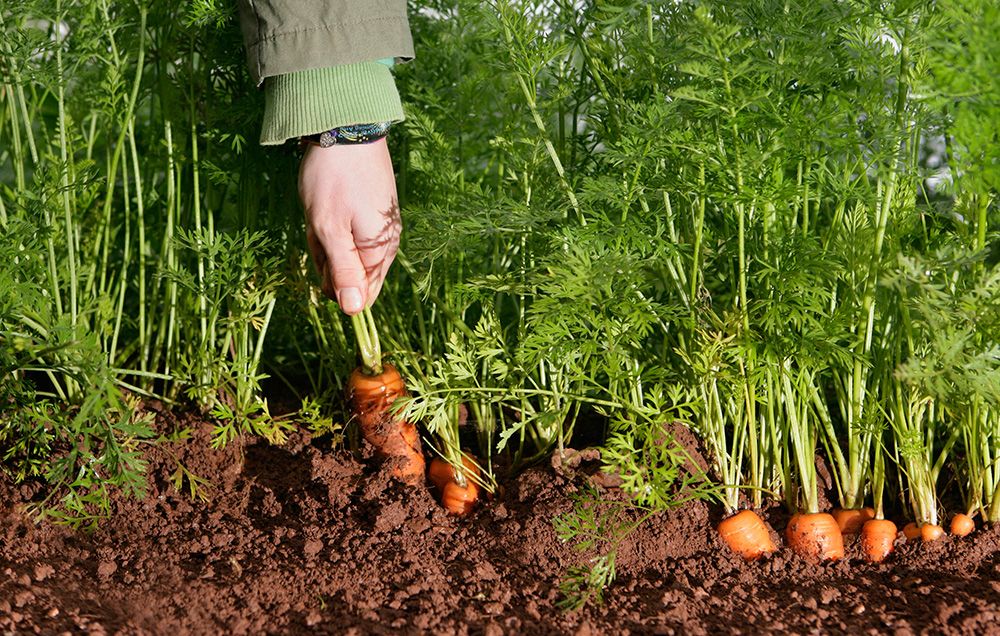
A significant crop of root vegetables is the carrot. Additionally, carrots are grown all over India. Carrots with an orange colour contain carotene. Carrots’ green leaves are packed with vitamins, minerals, proteins, and other nutrients that are good for feeding animals. Carrots’ green leaves can also be used as poultry fodder. The states of Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Punjab, and Haryana are the primary producers of carrot farming.
Table of Contents
Weather Conditions
The carrot is primarily a cold-climate crop, And its seed is important this cable can grow well at a temperature of 7.5 to 28 °C. The temperature has a significant impact on the growth of the roots as well as their colour. The roots are small but have the optimum colour at 15-20 °C. Various types respond differently to climate. European cultivars need 4.8 to 10 °C to 0-grade temperature during root formation for 4-6 weeks.
Suitability of Soil
Growing carrot farming is beneficial on loamy land. The field’s soil should be quite friable when planting is done. Because of how well-formed the roots are, drainage of water from the earth is crucial.
Land Preparation
The field should first be dug up twice with a victory plow and then dug up three to four times with an indigenous plow. The soil should be friable up to a depth of 30 cm after every plowing.
Variety of Carrots:

Pusa Kesar
This one is the greatest red carrot farming. Small leaves and tall, attractively reddish roots with a narrow base.
Ghali
With orange flesh, a short top, and a high level of carotene, it is a hybrid carrot. Carrot farming can be sown early and up until October, August, and September. In the field, the seed is created. The yield is 250–300 quintals per hectare, and the crop is ripe 100–110 days after seeding.
Yamdagni Pusa
The regional hub of I.A.R.I., Katarine, developed this species. 150–200 quintals are produced per hectare.
Nantes
These carrots have cylindrical, orange-colored roots. The root’s midsection, which is delicate, sweet, and fragrant, matures in about 110–112 days. 100–125 quintals are produced per hectare.
Season for Sowing Carrot Farming
Between August and October, the Asian varieties are sown on the plains, and between October and November, the European varieties are planted. For a one-hectare area, 6–8 kg of seed is needed.
Sowing
In the form of seeds, carrot seeds are planted. On flat land, seeds are dispersed for this. A one-hectare field requires between 6 and 8 kg of seeds. Treat these seeds before scattering them across the region. The soil is softly tilled after the seeds have been scattered. As a result, the seed penetrates the earth quite deeply. Then, using the plow, the ridges are formed into beds. The crop is then sprayed with water. Carrots of Asian varietals are cultivated between August and October, and European varieties are sown between October and November.
Irrigation and Weed Control
Apply 30 kg of nitrogen and 30 kg of potash per hectare in a one-hectare field at the time of sowing, as well as 25–30 tonnes of optimum dung manure at the time of the last plowing. Apply 30 kg of nitrogen as a top dressing five to six weeks after planting.
Grassland and Fertilizers
Apply 30 kg of nitrogen and 30 kg of potash per hectare in a one-hectare field at the time of sowing, as well as 25–30 tonnes of acceptable dung manure at the time of the last plowing. Apply 30 kg of nitrogen as a top treatment five to six weeks after sowing.
Irrigation
After sowing, the first irrigation should be performed in the drain to keep the bunds moist. Thereafter, irrigation should be performed periodically. 8 to 10 days long. Watering should be done every four to five days during the summer. The yield should be high if the field doesn’t ever dry up.
Control of Weeds
Due to their negative impact on the growth and development of carrot plants, many weeds coexist with the crop of carrot farming and absorb nutrients and moisture from the soil, necessitating their removal from the field during weeding. Increase the intermediate distance by removing the necessary plants, and light weeding should be done close to the emerging roots.
Harvesting and Digging
When the carrot roots are finished developing, they should be harvested. When digging, there should be a sufficient amount of water in the field. In February, you should also dig the roots. Before putting the roots on the market, they should lastly receive a thorough washing. The variety affects the yield. Asian plant varieties produce more. For instance, Pusa’s yield
Pusa Medhaali produces 250–300 quintals per hectare, variety produces 300–350 quintals per hectare, and Nantes variety produces 100–112 quintals per hectare.
Conclusion
In India, growing carrot farming is a lucrative industry, and we may increase revenue by using cutting-edge farming equipment like a power weeder. Keep in touch with us if you want to learn more about successful Indian crops and carrot farming.